1.Introduction of ceramic monolith
Ceramic monolith plays a crucial role in RTO. With the development of RTO, the types and geometric structure of heat storage monolith have undergone significant changes. Initially, the researchers used elliptical pebbles as the thermal storage materials, believing that they can efficiently store heat energy and are relatively easy to obtain. However, the pebbles have the problems of poor ventilation and easily compressing the gaps, resulting in poor ventilation and affecting the efficiency. In addition, pebbles are not resistant to high temperature and temperature fluctuations, and are prone to breakage, which could have negative impacts on equipment efficiency. Later, ceramic saddle rings became the choice for a new type of heat storage media, solving the problem of pebbles. This type of heat storage material ensures the consistency in the gaps, improve the uniformity of material, and significantly improve the efficiency of heat storage process. Nowadays, modern RTO system typically use honeycomb ceramic monolith fillers with high recovery efficiency and low airflow resistance, including regularly arranged fillers and dispersed particle fillers, as well as other shapes like spherical, tubular, corrugated plate and saddle shaped ceramic monolith. As shown in table 2-1, honeycomb ceramic monolith is usually preferred, because it has a short commutation cycle, smaller resistance loss, larger specific surface area and higher heat transfer efficiency. Besides, it has a smaller coefficient of thermal expansion, a more compact structure and a longer service life.
Performance | Spherical ceramic monolith | Honeycomb ceramic monolith |
Specific surface area | Small | Large |
Density | Honeycomb ceramic is 1/10 of ceramic ball | |
Heat storage and release capacity | Low | High |
Commutation cycle | 180-300s | 30-60s |
Resistance of airflow | Large | Small |
Uniformity of medium temperature | Nonuniform | Uniform |
Service life | No difference | No difference |
Material requirements | Low | High |
Accumulate dust | Easy | Difficult |
The material of heat storage monolith is crucial. In RTO equipment, metal media are not suitable because the high-tempera working condition could damage metal materials. The ceramic monolith became the first choice, including materials such as mullite and cordierite. Ceramic monoliths have multiple advantages, such as oxidation resistance, high temperature resistance, chemical corrosion resistance, strong thermal conductivity and good thermal shock resistance, and relatively low cost, so they are widely used.
2.Analysis for ammonium salt blockage problem in ceramic monolith
Due to the periodic heat storage and release in RTO, ceramic monoliths are periodically exposed to both high and low temperature environment and are prone to phenomena such as pore collapse, rupture and agglomeration. In practical applications, it has been found that in addition to the phenomenon of blockage caused by ceramic monolith itself, the composition and treatment process can also cause the blockage of ceramic monolith. Below, we will take actual engineering projects as samples to analyze in detail the composition and formation mechanisms that cause ammonium salt blockage of ceramic monolith.
2.1 Exhaust gas composition
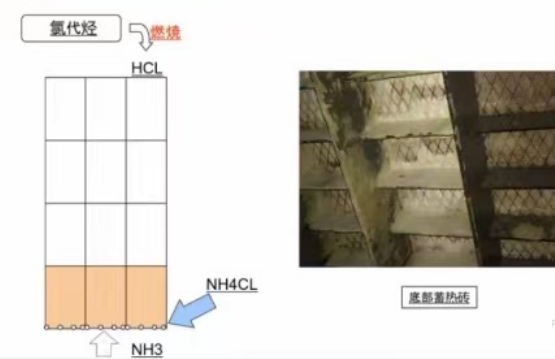
A pharmaceutical company in Hubei Province mainly produces Vitamins and other drugs through fermentation technology. The main compositions of exhaust gas are ethanol, benzene, toluene, ethyl acetate, triethylamine, oxazole, HCl, heptacycline, n-butanal, methane, hydrogen sulfide, ammonia, etc. The total flow rate is 50000 m³/h. During the production process, the fermentation workshop will generate a large amount of exhaust gas and wastewater, among which the wastewater will produce a strange odor when discharged into the sewage treatment station for treatment. The "spray+RTO" process is used to treat these two parts of exhaust gas and discharge them after reaching the standard. After a month of stable operation of the process, the RTO inlet and outlet pressure difference gauge showed a pressure difference greater than 4500Pa, so the equipment was shut down for maintenance. During maintenance, it was found that there was obvious blockage in the ceramic monolith, as shown in Figure 3.1.


Figure3.1 Comparison of ceramic monolith before and after being blocked by ammonium salt
2.2 Analysis of blockage caused by ammonium salt
Ammonium salt blockage is one of the key problems faced by ceramic monolith. The main reason for the formation of ammonium salts is that the exhaust gas contains compositions that are prone to forming ammonium salt after RTO incineration, which form in the low-temperature area below the ceramic monolith.
The ammonium salts that cause blockage of thermal storage systems generally include ammonium chloride, ammonium sulfate, ammonium carbonate, ammonium nitrate, and triethylamine hydrochloride.
Specifically, the following are the properties and effects of different ammonium salts
(1) Ammonium chloride: Ammonium chloride is a white crystal that is easily soluble in water, but insoluble in ethanol and ether. Decomposition into ammonia and hydrogen chloride at high temperatures can cause corrosion to RTO, especially in the low-temperature region of RTO.
(2) Triethylamine hydrochloride: Triethylamine is an organic compound that forms triethylamine hydrochloride with HCl. This substance is irritating and easily hygroscopic.
(3) Ammonium sulfate: Ammonium sulfate is an acidic salt that easily decomposes into ammonia and ammonium bisulfate at high temperatures, and is also hygroscopic. This salt can cause acidic conditions in the RTO device and damage the equipment.。
(4) Ammonium nitrate: Ammonium nitrate decomposes into ammonia, nitrogen dioxide, and water at high temperatures, which can lead to unstable gas composition, and its hygroscopicity can exacerbate the blockage problem of ceramic monolith.
(5) Ammonium carbonate: Ammonium carbonate is easily decomposed into ammonia, carbon dioxide, and water at high temperatures, and has high hygroscopicity, which has adverse effects on RTO devices.
According to the exhaust gas parameter table and on-site production process of this project in Hubei, as well as the analysis of the RTO site situation, the main reason for the blockage of the bottom of the ceramic monolith is caused by salt substances such as triethylamine hydrochloride
3.Control measures for ammonium salt crystallization
Ammonium salts have the following important characteristics:
(1) Ammonium salts are crystalline and ionic compounds;
(2) Ammonium salts are inorganic salts that are easily soluble in water;
(3) Ammonium salts are unstable and easily decompose when heated;
(4) Ammonium salts are mainly generated in the bottom layer of ceramics.
Based on its characteristics and practical engineering experience, the following measures are taken:
3.1 Prevention of ammonium salts formation
A. Classified collection and governance
a. Collect and treat ammonia containing exhaust gas separately, and do not mix with chlorine and sulfur containing exhaust gas.
b. Collect and treat chlorine containing exhaust gas separately, and do not mix with ammonia containing exhaust gas.
c. Collect and treat sulfur-containing exhaust gas separately, and do not mix with ammonia containing exhaust gas.
B. Take pre-treatment measures to reduce at the source
a. For exhaust gas containing both small amounts of ammonia and organic compounds such as chlorine, sulfur, and nitrogen, using acid washing, alkali washing, and demist processes to remove ammonia containing components from the exhaust gas at the front-end to reduce the generation of ammonium salts .
b. For exhaust gas containing both ammonia and a small amount of HCl and SO2, using alkaline washing+demist process to remove acidic components from the exhaust gas at the front end to reduce the generation of ammonium salts.
3.2 Slow down the generation of ammonium salts
According to the decomposition temperature, measures such an preheating, heat tracing, hot air blowing and insulation at the front pipeline to increase the temperature and reduce the generation of ammonium salts.
3.3 Slow down the blockage of ammonium salts
Using ceramic monoliths that are not easily blocked, such as honeycomb ceramics with large pore size and plate type ceramic, can effectively reduce the risk of ceramic monolith blockage.
3.4 Special structural design for RTO
A、Quick disassembly design of access door
Install access doors around the ceramic monoliths at the bottom of RTO. When ammonium salts occurs, the 12 access doors can be quickly opened and then use water to rinse the ceramics to dissolve the ammonium salts inside the ceramics. And the water can flow out from the bottom drainage outlet.
B、Thorough drainage structure of RTO body
RTO is equipped with a thorough structure at the bottom. When flushing the ceramics, the water can quickly discharge from the bottom drainage outlet. Every regenerative chamber is equipped with a drainage outlet, with a total of 12 drainage outlet for discharge. The outlet chamber is also equipped with a drainage outlet. All the water from the drainage outlets is converged to the main sewage pipeline for discharge.
3.5 Transformation measures and effects
Based on the on-site situation, there are two measures to reduce and remove triethylamine salts inside the ceramics.
Measure one: mixed high-temperature steam to the purging air pipeline
According to current testing verification, high-temperature steam can effectively dissolve and thermal decompose triethylamine hydrochloride substances accumulated in the bottom ceramics. When high temperature steam is introduced into the purging pipe, the frequency of rotary valve motor can be reduce to 30Hz, and the frequency of purging fan can be reduce to 30-35Hz, increasing the temperature of purging air and increasing the residence of steam in the purging area. This measure can better remove the triethylamine hydrochloride substances in the bottom ceramics. The system can also be modified to automatic flushing.
Measure two: prevent the generation of salts.
Before the exhaust gas enters RTO, add a pre-treatment system to reduce the concentration of triethylamine and prolong the blockage time of bottom ceramics. According to the in-site process, there are 7-12 feeding reaction per day (considering an average of 10), and for each feeding cycle, about 67kg of triethylamine will be lost. Considering the slightly soluble nature of triethylamine in water, the vast majority of triethylamine will evaporate into the exhaust gas. According to the main fan frequency of around 20Hz, the volume of exhaust gas is about 20000m³/h, and the concentration of triethylamine is 700mg/m³-1000mg/m³.
Transformation measure:
1. Separately collect the triethylamine containing exhaust gas of front end process and add acid wash pre-treatment system. Triethylamine is weakly alkaline, and after being sprayed and washed by dilute sulfuric acid, the concentration of triethylamine is greatly reduced. After acid washing pre-treatment system, the exhaust gas enters the existing alkali washing and water washing and demist system. After acid washing, there are triethylamine sulfate substances in the aqueous solution, which can enter the triethylamine recovery kettle to recycle and reuse triethylamine in the aqueous solution.
2. Separately collect the triethylamine containing exhaust gas in the front end process, change the existing pre-treatment system to acid washing and alkali washing and demist (with a backwash structure for demist). After acid washing, there are triethylamine sulfate substances in the aqueous solution, which can enter triethylamine recovery kettle to recycle and reuse the triethylamine in the aqueous solution.
The pretreatment renovation has been completed, and is currently in normal use. By retrieving data from the on-site pressure sensors, there has been no significant increase in system pressure loss since the pre-treatment system was put into operation (about one year ago).
4.Summary
For the chemical industry, our suggestion is that the design units should carefully develop the reasonable treatment plan and fully under the enterprise’s exhaust gas volume, composition, concentration and emission patterns when carrying out process deepening design. Especially for the cases where the exhaust gas contains multiple compositions such as halogenated hydrocarbons, ammonia and organic amines, priority should be given to the classification, collection and treatment of organic and inorganic exhaust gas. If complete separation is not possible, the exhaust gas enters RTO should be purified in stage by pre-treatment and post treatment devices according to the specific exhaust gas working condition to avoid issues such as ammonium salt blockage, corrosion, excessive emission of secondary pollutants.
The successful operation of this project provides valuable experience and reference for the RTO system design of other fine chemical enterprises. We believe that this project will have a profound impact in the fields of environmental protection and exhaust gas treatment, contributing to a cleaner, sustainable industrial development.